# Transformers-Part1
Attention is All your Need
最近服务器大量跑计算,正好有时间,把这个非常出名的 Transformers 好好看看,结果就发现他过于抽象,还是归因于自己对于 python 的类、实例、函数认识不清,对于 Torch 还有深度学习基础架构不熟悉。趁这个机会正好好好学习一下。主要就是首先简单记录一下 Transformers 的基础架构,再深入看看基于 Torch 的 Transformers 源码。文中肯定是有纰漏的,有缘人看到请帮忙指正…
# Transformers 模型架构
乍一看这个东西挺唬人的,把它分解开来看还是较为简单。左边部分为 Encoder 层,右边则为 Decoder 层。
Encoder 接受数据及其位置编码(NLP 应用中),数据经过 Embedding 后则进入 Encoder 层。Encoder 层由 N 个 EncoderLayers 组成,每个 layers 之间是相连的,EncoderLayers 则包括多头注意力层(Multi-Head Attention),Add & Norm,Feed Fordward 等小组件组成。
Decoder 接受数据及其位置编码,与 Encoder 的不同在于,Decoder 同样接受来自 Encoder 的 output。Decoder 层由 N 个 DecoderLayers 组成,每个 layers 之间相互链接,其中的组件同样包括多头注意力层(Multi-Head Attention),Add & Norm,Feed Fordward 等小组件。
虽然这里有一大堆让人看着就不太明白的词汇,但其实就可以发现整个 Transformers 架构是由很多小组件类似于拼积木组成。
# Multi-Head Attention
关于注意力机制的原理可以看 B 站 3blue1brown 的视频【官方双语】直观解释注意力机制,Transformer 的核心 | 【深度学习第 6 章】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili。起初的注意力机制将注意力汇聚的输出计算成为值的加权和。许多博客也有解释,通过 Query 与 Key 的注意力汇聚(即,给定一个 Query,计算 Query 与 Key 的相关性,然后根据 Query 与 Key 的相关性去和对应的 Value 进行相乘)实现对 Value 的注意力权重分配,生成最终的输出结果。给我的感觉就是 Attention 还是一种计算键值对相关性的一种形式。而当 Query,Key,Value 均来自同一个数据的时候,神奇的事情发生了,这时的 Query,Key,Value 相同,即计算自己跟自己的相关性,那么抽像的来说就是对数据自身包含的规律进行了学习,是一种将单个序列的不同位置相关联的注意力机制。
注意力机制源码,参考
1 | import math |
从源码来看就是首先对数据进行三次线性变换(Pytorch nn.Linear () 的基本用法与原理详解及全连接层简介 - CSDN 博客,包括了权重 W 矩阵的初始化),生成 Query,Key,Value 三个 tensor 对象,接着根据 Attention 公式进行计算。
而多头注意力机制是在自注意力机制的基础上发展起来的,是自注意力机制的变体,旨在增强模型的表达能力和泛化能力。它通过使用多个独立的注意力头,分别计算注意力权重,并将它们的结果进行拼接或加权求和,从而获得更丰富的表示。
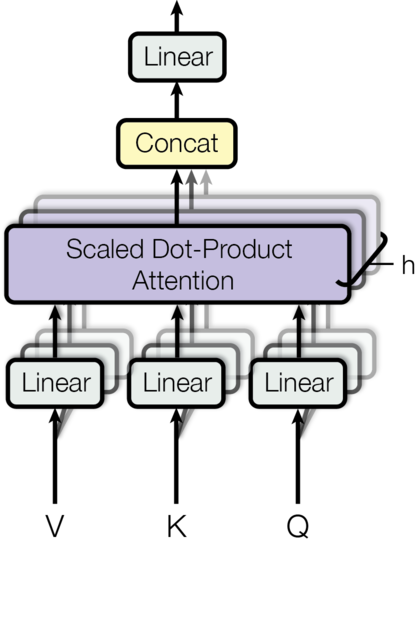
1 | class MutiHeadSelfAttentionFormal(nn.Module): |
# Transformers
因此 Transformers 可分块写为
-
MHA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65import torch
import math
import torch.nn as nn
import copy
# 多头注意力
class MutiHeadSelfAttentionFormal(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, head_num, attentnion_dropout=0.1):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_dim = dim
self.head_num = head_num
self.head_dim = dim // head_num # (head_num * head_dim = dim)
self.q_proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim) # (dim, head_num * head_dim) 后面可以用split拆分
self.k_proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.v_proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.attentnion_dropout = nn.Dropout(attentnion_dropout)
def forward(self, query, key, value, attention_mask=None, mask_type="Encoder"):
"""
In Encoder: query = key = value = X;
in Decoder: query = X, key = value = m
"""
# X (batch, seq, hidden_dim)
batch, seq_len, _ = query.size()
Q = self.q_proj(query)
K = self.k_proj(key)
V = self.v_proj(value) # (b, s, h)
# (b, s, h) -> (b, head_num, s, head_dim) # (head_num * head_dim = h)
q_state = Q.view(batch, seq_len, self.head_num, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
k_state = K.view(batch, seq_len, self.head_num, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
v_state = V.view(batch, seq_len, self.head_num, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
# (b, head_num, s, s)
attention_weight = torch.matmul(
q_state, k_state.transpose(-1, -2)
)/math.sqrt(self.head_dim)
if attention_mask is None:
if mask_type == "Encoder":
attention_mask = torch.ones_like(attention_weight) # 全是1的矩阵
elif mask_type == "Decoder":
attention_mask = torch.ones_like(attention_weight).tril() # 全是1的矩阵构建下三角矩阵
else:
if mask_type == "Encoder":
pass
elif mask_type == "Decoder":
attention_mask = attention_mask.tril()
attention_weight = attention_weight.masked_fill(attention_mask==0, float('-1e20'))
# print(attention_weight.shape)
attention_weight = torch.softmax(attention_weight, dim=-1)
attention_weight = self.attentnion_dropout(attention_weight)
output_mid = attention_weight @ v_state # (b, head_num, s, head_dim)
output_mid = output_mid.transpose(1, 2).contiguous() # 链接不同header
output_mid = output_mid.view(batch, seq_len, -1)
output = self.out_proj(output_mid)
return output -
Feed-forward network 前馈神经网络(FFN)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20# FFN
class ffn(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, ffn_dropout_rate=0.1):
super().__init__()
# ffn Position-wise Feed-Forward Networks(FFN) 升维 -> 降维 -> LayerNorm
self.up_proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim*4)
self.act_fn = nn.GELU() # 可换用RELU
self.down_proj = nn.Linear(dim*4, dim)
self.drop_ffn = nn.Dropout(ffn_dropout_rate)
#self.ffn_ln = nn.LayerNorm(dim, eps=0.0000001) # smooth
def forward(self, X):
# ffn
up = self.up_proj(X) # 升维
up = self.act_fn(up) # 激活 GELU
down = self.down_proj(self.drop_ffn(up)) # 降维
#down = self.drop_ffn(down) # drop
# add & Norm
return down -
Encoder
将 Encoder 的各个组分连接起来
1
2
3
4
5# Function clones modules
# useful function
def clones(module, N):
"Produce N identical layers."
return nn.ModuleList([copy.deepcopy(module) for _ in range(N)])1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9# add & norm
class add_and_norm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, add_dropout_rate=0.1):
super().__init__()
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim, eps=0.0000001)
self.add_dropout = nn.Dropout(add_dropout_rate)
def forward(self, X, sublayer):
return X + self.add_dropout(sublayer(self.norm(X)))Encoder 结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37# Encoder
class EncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, self_attn, self_ffn):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_dim = dim
self.self_attn = self_attn # attention layer
self.self_ffn = self_ffn # ffn layer
self.add_norm_layers = clones(add_and_norm(dim), 2) # add and norm layer
def forward(self, X, mask):
# add & norm结构的forward接受sublayer为函数对象
# attention layer 则需要多个参数X于mask,因此调用了lambda构造函数
s1 = self.add_norm_layers[0](X, lambda X: self.self_attn(X, X, X, mask))
s2 = self.add_norm_layers[1](s1, self.self_ffn) # FFN
return s2
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, self_attn, self_ffn, N=6):
"""
dim: input hidden dim;
self_attn: MHA object;
self_ffn: FFN object;
N: layers number
"""
super().__init__()
self.layer_list = clones(EncoderLayer(dim, self_attn, self_ffn), N)
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim, eps=0.0000001)
def forward(self, X, mask=None):
"Pass the input (and mask) through each layer in turn."
for m in self.layer_list:
X = m(X, mask) # 每个EncoderLayer构建模型
print(X.shape)
output = self.norm(X)
return output -
Decoder
Decoder 跟 Encoder 的结构类似,只是组合方式不一样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42# Decoder
class DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, self_attn, src_attn, self_ffn):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_dim = dim
self.self_attn = self_attn
self.src_att = src_attn
self.self_ffn = self_ffn # 这里的ffn实际为 ffn + add & Normal
self.add_norm_layers = clones(add_and_norm(dim), 3) # add and norm layer
def forward(self, X, memory, src_mask=None, tgt_mask=None):
m = memory
# step1 attention
s1 = self.add_norm_layers[0](X, lambda X: self.self_attn(X, X, X, src_mask))
# step2 attention with memory
s2 = self.add_norm_layers[1](s1, lambda X: self.self_attn(s1, m, m, tgt_mask))
# ffn
s3 = self.add_norm_layers[2](s2, self.self_ffn)
return s3
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, self_attn, src_attn, self_ffn, N=6):
"""
dim: input hidden dim;
self_attn: MHA object;
self_ffn: FFN object;
N: layers number
"""
super().__init__()
self.layer_list = clones(DecoderLayer(dim, self_attn, src_attn, self_ffn), N)
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim, eps=0.0000001)
def forward(self, X, memory, src_mask=None, tgt_mask=None):
"Pass the input (and mask) through each layer in turn."
for m in self.layer_list:
X = m(X, memory, src_mask=None, tgt_mask=None) # 每个DecoderLayer构建模型
print(X.shape)
output = self.norm(X)
return torch.softmax(output, dim=-1) -
Test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25# test NB!
c = copy.deepcopy
attention_mask = (
torch.tensor(
[
[0, 1],
[0, 0],
[1, 0]
])
.unsqueeze(1)
.unsqueeze(2)
.expand(3, 8, 2, 2)
)
X = torch.rand(3, 2, 128)
# module init
attn_net = MutiHeadSelfAttentionFormal(128, 8)
ffn_net = ffn(128)
Encoder_net = Encoder(128, c(attn_net), c(ffn_net))
Decoder_net = Decoder(128, c(attn_net), c(attn_net), c(ffn_net))
# run
E1 = Encoder_net(X, attention_mask)
D1 = Decoder_net(X, E1)
到此为止我们有了 Transformers 的基础架构,后面再仔细看看 Embedding 与 Training 部分
# Reference
The Annotated Transformer
注意力机制综述(图解完整版附代码) - 知乎
Pytorch nn.Linear () 的基本用法与原理详解及全连接层简介 - CSDN 博客
Transformer 源码详解(Pytorch 版本) - 知乎
chaofa 用代码打点酱油的个人空间 - chaofa 用代码打点酱油个人主页 - 哔哩哔哩视频